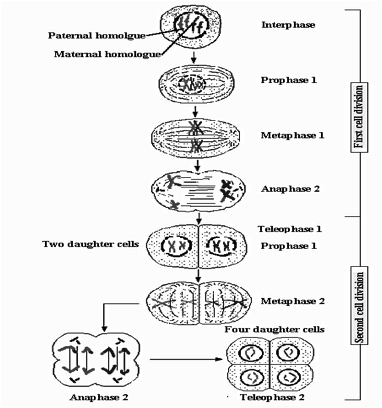
A type of nuclear and cell division in which the number of chromosomes is reduced from diploid to haploid (i.e., they are halved). This means it gives rise to four reproductive cellar or gametes, each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. It consists of two consecutive divisions: separation of homologous chromosomes and of the chromatids. The first division (the actual reduction division) is accounted for by interphase, early, mid and late prophase, the first metaphase, the first anaphase and the first teleophase, resulting in half of the original chromosomes. The second division covers the second metaphase, the second anaphase and the second teleophase, during which the daughter cells divide by mitosis and the four haploid (daughter) cells are produced (see figure below).